Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic panels, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They are an important technology in the field of renewable energy, as they provide a clean and sustainable source of electricity that does not rely on fossil fuels.
The basic building block of a solar panel is the solar cell, which is made of semiconductor materials such as silicon. When sunlight strikes the cell, it causes the electrons in the semiconductor to move, creating a flow of electricity. Several solar cells are connected together to form a solar panel.
Solar panels can be used in a variety of applications, including powering homes and businesses, as well as in large-scale solar power plants. They can also be used in off-grid systems, such as in remote areas where there is no access to the power grid.
One of the main advantages of solar panels is that they produce electricity with no greenhouse gas emissions, making them a clean and environmentally friendly source of energy. They also require very little maintenance, and can last for decades with proper care.
Another advantage of solar panels is that they can be installed on a variety of surfaces, including rooftops, walls, and even on the ground. This makes them a versatile source of energy that can be used in both urban and rural areas.
Solar panels are becoming increasingly cost-competitive with traditional sources of energy, such as coal and natural gas. The cost of solar panels has decreased significantly in recent years, making them more affordable for both residential and commercial customers.
What are benefits of Solar Panels?
- They are a clean and renewable source of energy. They do not produce any emissions or pollution, unlike fossil fuels.
- They are relatively low maintenance. Once installed, they require very little upkeep.
- They can save homeowners money on their electricity bills.
- They can help reduce dependence on fossil fuels and decrease the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- They can be used in remote or off-grid locations where it may be difficult or expensive to connect to the power grid.
How much it cost to install solar panel in India?
The cost of installing solar panels in India can vary depending on several factors, such as the size of the system, the location, and the type of panels and equipment used. However, on average, the cost of a residential solar panel system in India ranges from 70,000 to 2,50,000 INR depending on the size of the system and the specific equipment used. It’s also important to note that there are various government subsidies and incentives available that can help lower the cost of a solar panel system in India.
Who should install solar panels?
Solar panels can be installed by anyone who is interested in generating their own clean and renewable energy. They are particularly beneficial for:
- Homeowners who want to reduce their electricity bills and save money on energy costs in the long run.
- Businesses and organizations that want to reduce their carbon footprint and be more environmentally friendly.
- People who live in remote or off-grid locations where it may be difficult or expensive to connect to the power grid.
- People who want to be less dependent on fossil fuels and contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
- People who want to invest in a long-term, sustainable energy solution.
It’s also worth noting that many countries have various Government subsidies, tax benefits and other incentives for installing solar panels which makes it more viable for the users.
Who discovered solar panel?
The history of solar panels can be traced back to the 19th century when French scientist Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic effect, which is the basic principle behind the operation of solar panels. In 1839, Becquerel discovered that certain materials, such as selenium, produced an electric current when exposed to light. This was the first step towards the development of solar cells, which are the building blocks of solar panels.
However, it wasn’t until the 20th century that the development of solar panels really took off. In the early 1900s, several scientists and engineers began experimenting with different materials and designs for solar cells. One of the most notable of these early pioneers was American inventor Charles Fritts, who created the first solar cell made of selenium in 1883.
It wasn’t until the 1950s that the first practical solar cell was developed. Researchers at Bell Labs in the United States created a solar cell with an efficiency of 6%, which was a significant improvement over previous designs. This breakthrough led to the development of the first commercial solar panels, which were used primarily in space applications.
In the decades that followed, the efficiency of solar cells continued to improve, and the cost of producing solar panels began to decrease. This led to the widespread adoption of solar panels in various applications, including residential and commercial power generation.
In conclusion, the discovery of solar panels is a result of the hard work and contributions of many scientists and engineers over the course of several decades. The discovery of photovoltaic effect by Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel in 1839 was the initial step and the invention of solar cells by Charles Fritts in 1883 and the practical solar cell by Bell Labs in the 1950s are some of the most notable milestones in the history of solar panel technology. Today, solar panels are a vital source of clean and renewable energy, and their use is expected to continue to grow in the future.
Life of Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel
Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel was a French physicist and one of the pioneers of the study of photovoltaics, the technology behind solar panels. He was born in Paris on December 15, 1820, and was the son of Antoine César Becquerel, a well-known scientist in his own right.
Becquerel began his scientific career studying the properties of light and electricity. In 1839, he discovered the photovoltaic effect, which is the basic principle behind the operation of solar cells and solar panels. He discovered that certain materials, such as selenium, produced an electric current when exposed to light. This was a significant breakthrough in the field of photovoltaics and laid the foundation for the development of solar cells and solar panels.
Throughout his career, Becquerel continued to study the properties of light and electricity, and he made many other important contributions to science. He was particularly interested in the phenomenon of fluorescence, and he discovered that certain materials, such as quinine, emitted light when exposed to ultraviolet light. This work laid the foundation for the study of luminescence and the development of modern light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
Becquerel was also a skilled experimentalist and was known for his meticulous and thorough approach to research. He published many papers on his work and was recognized by his peers for his contributions to science. He was elected to the French Academy of Sciences in 1857, and in 1875 he was awarded the Royal Society’s Rumford Medal in recognition of his work on the photovoltaic effect.
Becquerel died on October 18, 1891, in Paris. He was honored for his contributions to science, and his legacy continues to this day in the form of the Becquerel Prize, which is awarded annually by the European Commission for outstanding contributions to the field of photovoltaics.
Life of Charles Fritts
Charles Fritts was an American inventor and one of the pioneers of the development of solar cells, the building blocks of solar panels. He is credited with creating the first solar cell made of selenium in 1883, which marked an important step towards the practical use of solar energy.
Fritts was born in New York City in 1853 and began his career as an electrician. He was interested in the properties of light and electricity, and he began experimenting with different materials and designs for solar cells in the early 1880s. In 1883, he created the first solar cell made of selenium, which had an efficiency of less than 1%. While this was a relatively low efficiency compared to modern solar cells, Fritts’ invention was a significant breakthrough at the time and marked the first practical application of the photovoltaic effect.
Fritts continued to work on improving the efficiency of his solar cells and in 1888, he published a paper describing his latest design, which had an efficiency of about 4%. He also developed a process for producing large quantities of solar cells, which helped to make them more affordable.
Despite his pioneering work in the field of solar energy, Fritts did not receive much recognition during his lifetime. His work was largely overshadowed by the more well-known scientists and engineers of the time, such as Alexander Graham Bell and Thomas Edison. However, in recent years, Fritts has been acknowledged for his contributions to the field of photovoltaics and his role in the development of solar cells and solar panels.
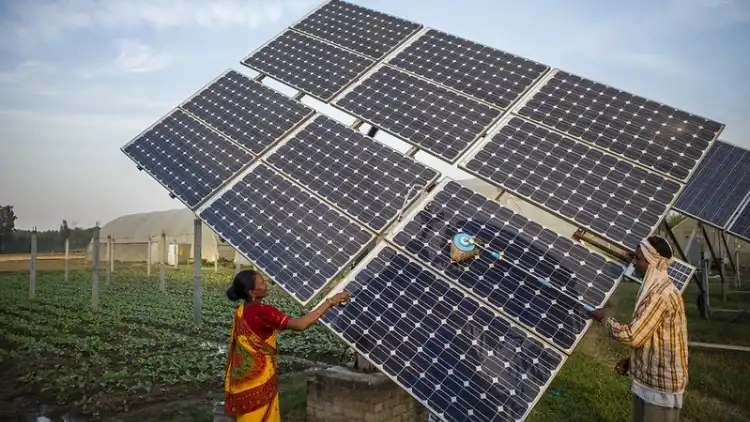
Solar Power and Solar Panels in India
Solar power in India has grown significantly in recent years, making it one of the leading nations in the world in terms of installed solar capacity. The Indian government has set ambitious targets for the growth of solar power, and the country is well on its way to achieving those goals.
One of the main drivers of solar power in India is the country’s large and growing energy needs. India is the world’s third-largest energy consumer, and its energy consumption is expected to triple by 2040. This has led to a strong need for renewable energy sources, such as solar power, to help meet the country’s energy demands.
The Indian government has implemented a number of policies and programs to promote the growth of solar power. One of the most important of these is the National Solar Mission, which was launched in 2010 with the goal of deploying 20 GW of solar power by 2022. The mission has been successful in driving the growth of solar power in India, and the country is on track to exceed its target.
The Indian government has also implemented a number of financial incentives to encourage the development of solar power, such as subsidies and tax breaks for solar projects. This has helped to make solar power more affordable, which has led to an increase in the number of solar projects being developed.
In addition to government policies, the private sector has also played an important role in the growth of solar power in India. Many Indian companies have invested in solar power, and the country now has a thriving solar industry. This has led to the creation of many jobs and has helped to boost the country’s economy.
Despite the progress that has been made, there are still challenges to be overcome in order to fully realize the potential of solar power in India. One of the main challenges is the lack of infrastructure and transmission lines, which makes it difficult to connect remote solar projects to the grid. Another challenge is the lack of financing for solar projects, which makes it difficult for small and medium-sized enterprises to participate in the sector.
The economy of India
The economy of India is the fifth-largest in the world by nominal GDP and the third-largest by purchasing power parity. It is classified as a newly industrialized country and a developing economy, with an average annual growth rate of 7.5% between 2014 and 2019. India is one of the world’s fastest-growing major economies, and is expected to be one of the top three economic powers of the world over the next 10-15 years, alongside China and the United States.
One of the main drivers of India’s economy is its large and growing population. With over 1.3 billion people, India has a large and diverse consumer market, which has led to the growth of many industries, such as textiles, automobiles, and consumer goods.
Another important driver of India’s economy is its rapidly growing middle class. As more and more Indians move into the middle class, they are consuming more goods and services, which has led to increased demand for a wide range of products. This has helped to boost the country’s economy and create jobs.
The service sector is the largest contributor to India’s GDP, accounting for more than 55% of the country’s GDP. The sector includes a wide range of industries, such as finance, healthcare, and technology, and has been growing rapidly in recent years.
India’s agricultural sector is also a significant contributor to the country’s economy, although it has been facing challenges in recent years, such as low productivity and lack of access to technology. The government has been implementing various policies to address these issues and to increase the productivity of the sector.
The manufacturing sector is also an important contributor to India’s economy. The sector has been growing rapidly in recent years, driven by a combination of factors, such as the growth of the middle class, the rise of the service sector, and the increasing availability of technology.
Despite the progress that has been made, there are still challenges to be overcome in order to fully realize the potential of India’s economy. One of the main challenges is the lack of infrastructure, which makes it difficult to transport goods and people, and can limit the growth of certain industries. Another challenge is the lack of access to education and training, which can limit the potential of the workforce.
Population as resource in India
Youth can be considered a valuable resource for a country, as they have the potential to contribute significantly to the development and growth of a nation. The youth population, defined as those aged 15-24, makes up a significant portion of the total population in many countries, and their active participation in society can have a positive impact on the economy, politics, and culture.
One of the key ways in which youth can contribute to a country’s development is through their participation in the workforce. Young people bring energy and new ideas to the workplace, and they can play a vital role in driving innovation and productivity. They also have the potential to fill skills gaps in the labor market, and can help to drive economic growth.
Additionally, youth can play an important role in shaping the political and social landscape of a country. They have the ability to bring fresh perspectives and new ideas to the table, and can play a key role in driving social change and progress. They also have the potential to be active and engaged citizens, and can help to promote democratic values and institutions.
Furthermore, youth can also contribute to the cultural and creative life of a country. They have a unique perspective on the world, and can bring new and exciting ideas to the arts, music, and literature. They can also play an important role in preserving and promoting the cultural heritage of a country.
However, it is important to note that in order for youth to fully realize their potential as a resource for a country, they must have access to quality education, training, and employment opportunities. They also require a supportive environment that encourages their participation in the workforce, politics, and cultural life of the country.
The population of India is the second-largest in the world, with over 1.3 billion people as of 2021. India is a diverse country with a wide range of ethnic and linguistic groups, and has a rapidly growing population that is projected to reach 1.5 billion by 2030.
One of the main drivers of India’s population growth is its high fertility rate. The total fertility rate in India is 2.3, which is higher than the replacement level of 2.1. This has led to a large youth population, with over 50% of the population being under the age of 25.
Another driver of India’s population growth is its relatively young age structure. The median age in India is 27, which is lower than the global median age of 30. This means that a larger share of the population is in the reproductive age group, which contributes to the high fertility rate.
The population of India is also highly urbanized, with over 31% of the population living in urban areas. This is expected to increase in the future, as the country’s urbanization rate is among the highest in the world.
However, the population growth in India also poses several challenges. The rapid population growth has put a strain on the country’s resources, and has led to issues such as overcrowding, pollution, and shortage of housing. Additionally, the population growth has led to increased competition for jobs, which can make it difficult for people to find employment.
The government of India has implemented several policies to address the population growth, such as the National Population Policy (2000) and the National Health Policy (2017). These policies aim to improve access to family planning services, education and healthcare, and to create awareness about the importance of smaller family sizes.
What is National Population Policy (2000)?
The National Population Policy (NPP) of India was announced in 2000, with the goal of achieving a stable population by 2045. This policy outlines a comprehensive approach to addressing the country’s population growth, with a focus on improving access to family planning services, education, and healthcare.
One of the main objectives of the NPP is to provide universal access to reproductive and child health services. This includes increasing access to family planning methods, including modern methods such as contraceptives, as well as providing prenatal and postnatal care for mothers and infants. The policy also aims to reduce maternal and infant mortality rates, and to improve the overall health and well-being of women and children.
The NPP also aims to improve access to education and employment opportunities for women, as these are key factors in reducing fertility rates. By providing women with more opportunities for education and employment, the policy aims to empower them to make informed choices about their reproductive health and to have smaller families.
Another important aspect of the NPP is to create awareness about the importance of smaller family sizes. This includes educating the public about the benefits of family planning and the negative consequences of population growth, such as strain on resources and environmental degradation.
The policy also aims to improve the overall data management and monitoring system of family planning and population-related programs. It also encourages public-private partnership to provide quality services and to make them affordable to the people.
The NPP also emphasizes on the need of involving Panchayats (local government bodies) and NGOs (Non-Governmental Organizations) in the implementation of population-related programs and services. This is to make sure that the services reach the grassroots level and are provided to the people who need them the most.
What is National Health Policy (2017)?
The National Health Policy (NHP) of India was announced in 2017, with the goal of providing universal access to quality healthcare for all citizens. The policy outlines a comprehensive approach to addressing the country’s health needs, with a focus on improving access to healthcare services, promoting health and well-being, and achieving better health outcomes.
One of the main objectives of the NHP is to provide universal access to healthcare services. This includes increasing access to essential medicines and vaccines, as well as providing primary, secondary and tertiary healthcare services for all citizens. The policy also aims to improve the overall health and well-being of citizens, by addressing key health determinants such as nutrition, sanitation, and environment.
The NHP also aims to improve access to affordable and quality healthcare for all citizens, especially for vulnerable and marginalized communities. This includes increasing public spending on health, and making healthcare more accessible and affordable for low-income and rural populations. The policy also encourages the private sector to play a greater role in providing healthcare services, and to make sure that they are affordable and accessible to all.
Another important aspect of the NHP is to promote health and well-being. This includes creating awareness about the importance of good health and well-being, and providing citizens with the knowledge and skills they need to maintain good health. The policy also encourages the promotion of healthy behaviors such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and the avoidance of tobacco and alcohol.
The NHP also focuses on improving the overall quality of healthcare services, by strengthening the health system and focusing on key areas such as human resources, infrastructure, and technology. The policy also aims to make sure that healthcare services are evidence-based, and that they are provided by well-trained and qualified healthcare professionals.
What is the vision of Prime Minister Narendra Modi?
Narendra Modi, the current Prime Minister of India, has a vision for the country that is grounded in the principles of development, growth, and progress. He has often spoken about his vision for a “New India” that is strong, prosperous, and inclusive, and that is able to take its rightful place on the global stage.
One of the key components of Modi’s vision is the idea of development. He has emphasized the need to create a strong and modern infrastructure in India, and has launched several initiatives aimed at improving transportation, power, and communication networks. He has also focused on developing key sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and services, with the goal of creating jobs and boosting economic growth.
Another important aspect of Modi’s vision is the idea of growth. He has emphasized the need to create an environment that is conducive to business and investment, and has taken several steps to reform the economy and make it more competitive. He has also focused on promoting exports and encouraging foreign investment, with the goal of making India a hub for global trade and commerce.
Modi’s vision also includes the idea of progress. He has emphasized the need to make India a leader in science and technology, and has launched several initiatives aimed at promoting research and innovation. He has also focused on improving the quality of education and skill development, with the goal of creating a highly skilled workforce that can compete globally.
Modi’s vision also includes the idea of inclusion. He has emphasized the need to create an inclusive society that is free from discrimination and inequality, and has launched several initiatives aimed at empowering marginalized communities and promoting social justice. He has also focused on promoting gender equality and empowering women, with the goal of creating a more equal and equitable society.
What is the vision of BJP?
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) is a political party in India that has a clear and distinct vision for the country. The party’s vision is rooted in the principles of nationalism, conservative, and right-wing ideology, and it seeks to promote the values of Hinduism, cultural and spiritual heritage of India as well as its economic growth and development.
One of the key components of the BJP’s vision is the idea of nationalism. The party believes in the strong, united and self-reliant nation, which is sovereign and independent in its decision-making. The party also emphasizes the need to protect the country’s territorial integrity and defend its sovereignty from external threats.
Another important aspect of the BJP’s vision is the idea of cultural and spiritual heritage. The party believes in the rich cultural and spiritual heritage of India, and seeks to promote and preserve it for future generations. The party also emphasizes the need to protect the rights and interests of the Hindu majority in India, and to ensure that the country’s heritage and culture are not threatened by external influences.
The BJP’s vision also includes the idea of economic growth and development. The party has emphasized the need to create an environment that is conducive to business and investment, and has taken several steps to reform the economy and make it more competitive. It also focuses on improving the quality of life of the people by providing them with basic amenities and infrastructure.
The party’s vision also includes the idea of good governance. The party seeks to promote transparency, accountability and efficiency in the government’s functioning and reduce corruption. The party believes in the empowerment of people through decentralized decision-making and participatory governance.
Status of India in the World
India, a land of ancient civilization and rich cultural heritage, is rapidly emerging as a power in the world. With a rapidly growing economy and a population of over 1.3 billion, India is poised to play a significant role in shaping the global political and economic landscape.
One of the key factors contributing to India’s emergence as a power is its rapidly growing economy. India is the fifth-largest economy in the world and is projected to become the third-largest by 2030. The country has a diverse and rapidly expanding industrial base, and is home to a large number of small and medium-sized enterprises. The government has also been taking steps to improve the ease of doing business and attract foreign investment, which has further fueled economic growth.
Another factor that has contributed to India’s emergence as a power is its strategic location. India is situated at the crossroads of major global trade routes, making it a key player in the global economy. The country’s ports, airports, and infrastructure have been developed to handle large volumes of trade and transportation. India is also playing an increasingly important role in regional and global security, with a strong military presence in the Indian Ocean region and a growing number of strategic partnerships with other countries.
India’s human resources are also a significant factor in its emergence as a power. The country has a large and educated workforce, and a rapidly growing middle class. This has led to the growth of a consumer market that is now among the largest in the world. The country also has a large pool of highly skilled professionals in fields such as engineering, IT, and healthcare.
The country has also been active in the field of diplomacy and has been trying to become a leader in the region and the world. India has been actively participating in international organizations and forums and is a member of the G20 and the BRICS. The country has also been trying to play a larger role in the United Nations and has been seeking a permanent seat in the UN Security Council.
Relation of India with US, Russia, China and Pakistan
India, the world’s largest democracy and a rapidly emerging economy, has complex and multifaceted relations with the United States, Russia, and China, three of the world’s most powerful nations. These relationships are shaped by a combination of historical, economic, and strategic factors, and they have a significant impact on the regional and global balance of power.
India’s relationship with the United States is one of the most important and dynamic in the world. The two countries have a long history of cooperation and partnership, and the relationship has grown stronger in recent years, particularly in the areas of trade, defense, and counter-terrorism. The United States has also been a strong supporter of India’s rise as a global power and has played a key role in India’s integration into the global economy.
India’s relationship with Russia, on the other hand, has a historical and strategic dimension. Russia has been a long-term supplier of military equipment to India, and the two countries have also cooperated in the fields of energy, space, and civil nuclear energy. However, in recent years, India has been diversifying its defense imports and seeking to reduce its dependence on Russia.
China, which shares a long and disputed border with India, is a major economic and strategic rival of India. The two countries have had a number of disputes over territory and resources, and their relationship has been marked by mistrust and competition. However, in recent years, the two countries have also sought to improve relations and increase economic cooperation.
India and Pakistan’s relationship is one of the most complex and contentious in the world. The two countries have a long history of conflict, dating back to the partition of British India in 1947 and the subsequent formation of the two independent nations of India and Pakistan. The relationship has been marked by a number of disputes, including the ongoing Kashmir conflict, and has resulted in several wars and military standoffs.
One of the main issues that has contributed to the strained relationship between India and Pakistan is the ongoing dispute over the region of Kashmir. Both countries claim the region as their own, and the issue has led to several wars and military standoffs. The situation in Kashmir remains tense, with ongoing cross-border militancy and human rights violations reported on both sides.
Another major issue that has contributed to the strained relationship between India and Pakistan is the issue of terrorism. Both countries have accused each other of supporting and harboring terrorist groups, and have been involved in a number of terrorist attacks. The most notable of these was the 2008 Mumbai terrorist attacks, which were planned and executed by a Pakistan-based terrorist group.
Despite these challenges, there have been some efforts in recent years to improve relations between India and Pakistan. The two countries have engaged in a number of peace talks and diplomatic initiatives, including the ongoing backchannel dialogue. These efforts, however, have not yet resulted in a significant breakthrough in the relationship.