The greatest gift of God to a woman is ability to become a mother. But, it’s really heart breaking when, after years of marriage a lady is unable to conceive and after diagnosis the doctor says you have PCOS.
Today Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) has become the major cause of infertility in women. Sometimes it is also called Stein Leventhal Syndrome. One in ten women is affected by it. A recent study conducted by Metropolis showed that around 27% of women aged between 15 to 30 years suffer from PCOS, a hormonal disorder. The only way to deal with it is to be aware of its symptoms and get treated on time.
WHAT IS POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME?
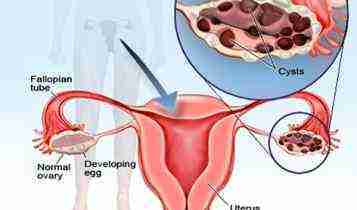
Let us understand what happens in PCOS. In women with PCOS, the level of male hormones, androgens is higher. The hormone imbalances in the body causes irregular ovulation or even lack of ovulation, making it hard to become pregnant. In detail, A woman has a pair of ovaries which produces female hormones (estrogens and progesterone) and some male hormones called androgens (testosterone).
The egg is released from each ovary every month alternatively. In each menstrual cycle, a follicle is supposed to break open and release a mature egg.
Thus, women having PCOS the follicles do not break, instead they stick around as a tiny cyst. These cysts itself produce androgens, which causes abnormalities in menstrual order and irregular ovulation or even lack of ovulation, making it hard to become pregnant and causes infertility.
SYMPTOMS OF POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME
- Irregular menstrual cycle: Women with PCOS have fewer periods or irregular periods. Some women may even stop having menstrual cycle.
- Too much hair growth: Due to high levels of androgens, and low levels of oestrogen and progesterone, women may have too much hair on face, chin or parts of body where men usually have hairs. This condition is called “hirsutism”. It effects 70% of women with PCOS.
- Acne: Women having PCOS have acne on face, chest and upper back
- Male pattern baldness: PCOS can cause hair loss or thinning hair or male pattern baldness in women.
- Skin tags: Due to PCOS, skin tags may occur which are excess flaps of skin in armpits or neck area.
- Weight Gain: Women with PCOS can gain excess weight can face trouble in loosing weight too.
- Difficulties in conception: A woman is unable to conceive, and even after conception she is at a greater risk, as high as 50% of miscarriage
- Heavy bleeding and pain: Painful periods and heavy bleeding is also one of the symptoms of PCOS.
CAUSES OF POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME
The exact cause of PCOS is not yet known but several factors play part for such condition
1. INSULIN RESISTANCE: Insulin is a hormone that is made by the pancreas in our body. Its main role is to control sugar level in blood. Another role of insulin is to act on ovaries to cause them produce male hormone testosterone. In PCOS, the woman’s body is resistant to the effect of normal levels of insulin, the condition is called insulin resistance. Hence, more insulin in the body is produced to keep blood sugar normal. 70% of women with PCOS have Insulin Resistance.
This raised level of insulin makes ovaries to produce more testosterone, which further interfere with normal development of follicles in the ovaries, as a result, many follicles tend to develop but often do not develop fully which causes period problems and reduced fertility. This is expected to be the major cause of Polycystic ovaries.
2. Luteinising Hormone (LH): This hormone is made by the pituitary glands, which are located in the base of the brain. In PCOS levels of Luteinising Hormone is quite high. It stimulates the ovaries to ovulate along with insulin to promote testosterone production.
3. LOW GRADE INFLAMMATION: Women with PCOS have a type of low grade inflammation (white blood cell production) that stimulates polycystic ovaries to produce androgens which can lead to heart and blood vessel problems.
4. HEREDITY: PCOS is common in women who have a family history of it. This heredity is also a factor in causing PCOS.
5. NUTRIENT DEFICIENCY: Wrong diet system, inadequate rest or sleep, lack of nutrients in food can also be the reason for polycystic ovaries. Medicines taken to treat some of other symptoms may affect your ability to get pregnant.
6. OBESITY AND OVERWEIGHT: Excess weight and obesity can make insulin resistance worse and level of insulin may rise further.
DIAGNOSIS OF POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME
For the diagnosis of PCOS, the doctor may ask for a medical history and conduct different test. Some of the tests are:
1. Physical Examination: A doctor will examine the patient physically which includes measurement of blood pressure, Body Mass Index (BMI). He may look for extra hair, acne, discoloration of skin and hair loss.

2. Pelvic Exam: Pelvic examination may be done to check if the ovaries are enlarged or swollen and also to examine signs of extra male hormones.
3. Ultrasound: It is an advanced technique to diagnose PCOS. It gives the clear picture of pelvic region and detect abnormal follicles and other problems in the uterus and ovaries.
HOW IS PCOS TREATED?
Treatment depends on the symptoms and whether a woman is planning for pregnancy. There is no cure for PCOS, but controlling it lowers the risk of infertility, miscarriages, diabetes and uterine cancer.

1. HEALTHY LIFESTYLE: Losing even 5% of body weight may improve the condition by reducing male hormone testosterone, which will improve the chances of ovulation. Further, it will reduce acne and excess hair growth. Regular exercise and food with low Glycemic Index (low GI) should be consumed, which will keep blood sugar levels steady. Limit carbohydrates and increase the intake of fruits, green vegetables and pulses in diet. Quit smoking, women who smoke have higher levels of androgens than women who do not smoke.
2. HORMONE THERAPY: If loosing weight does not start ovulation, the doctors may try medicines like birth control pills metformin or clomiphene to help ovulation.
3. REGULAR CHECK UPS: Regular check ups are very important to avoid further complications such as high blood pressure, uterine cancer and diabetes.
4. DRUGS THAT CONTROL ANDROGENS: Doctors may prescribe drugs or medications which control the androgen levels and helps in ovulation.