Since 2014, the European Union (EU) has taken a strong stance against Russia in response to Moscow‘s military intervention in Ukraine. The EU has implemented a series of sanctions aimed at targeting individuals, entities, and sectors of the Russian economy to put pressure on the Russian government and encourage a change in its behavior.
The initial round of EU sanctions was introduced in March 2014, following Russia’s annexation of Crimea. The measures included travel bans and asset freezes on Russian officials who were considered to be responsible for the annexation. Over time, these measures were expanded to include additional individuals and entities involved in the conflict in eastern Ukraine.
Subsequent rounds of EU sanctions have focused on key sectors of the Russian economy, such as energy, finance, and defense. These measures have limited access to EU markets and technology, as well as access to finance from EU institutions. The economic impact of the sanctions has been significant, with the value of the ruble falling sharply and economic growth in Russia slowing down.
In addition to the economic sanctions, the EU has implemented diplomatic measures against Russia, such as suspending political dialogue and cooperation in various areas. The EU has also provided economic and political support to Ukraine, including financial assistance and the signing of an Association Agreement.
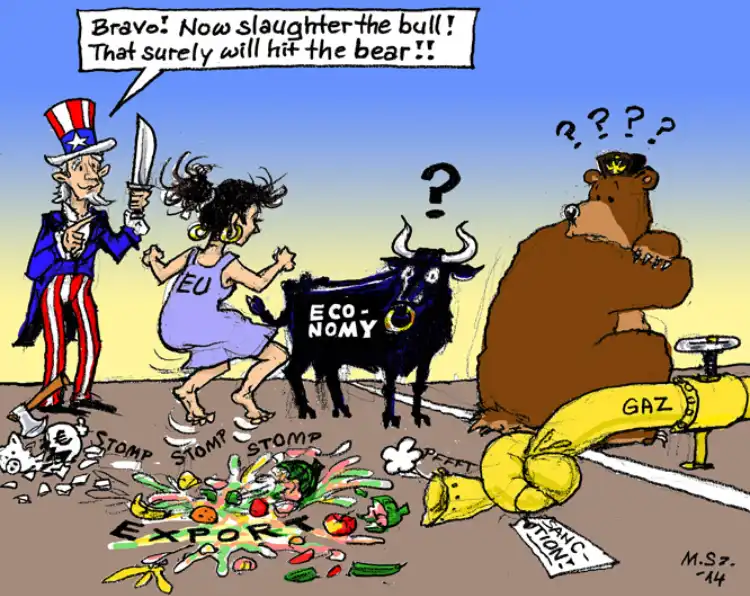
However, the effectiveness of the EU sanctions against Russia is a matter of debate. Although they have put pressure on the Russian government, they have also had negative consequences for EU businesses and citizens. Some EU member states have been more affected by the sanctions than others, depending on their economic and political ties to Russia.
Furthermore, the sanctions have not led to a resolution of the conflict in Ukraine or a change in Russian behavior. Russia has responded to the sanctions by imposing its own counter-sanctions on the EU, which have had negative consequences for EU businesses, particularly in the agriculture sector.
The ongoing tensions between the EU and Russia have also been complicated by other factors, such as Russia’s involvement in Syria and its alleged interference in the 2016 US presidential election. The EU has continued to coordinate its approach with the United States, which has also imposed sanctions on Russia.
The EU’s sanctions against Russia since 2014 represent a significant effort to apply pressure on the Russian government and encourage a change in its behavior. However, the impact of the sanctions on both sides remains controversial, and it is uncertain whether they will ultimately lead to a resolution of the ongoing tensions between the EU and Russia.
List of sanctions imposed by the European Union on Russia
The European Union (EU) has imposed several rounds of sanctions on Russia since 2014 in response to its actions in Ukraine.
The following is a list of the major sanctions imposed by the EU:
- March 2014: The EU imposes sanctions on individuals responsible for the annexation of Crimea, including asset freezes and travel bans.
- July 2014: The EU imposes restrictions on trade and investment in Crimea.
- July 2014: The EU imposes sanctions on Russian individuals and entities deemed responsible for the conflict in eastern Ukraine, including asset freezes and travel bans.
- September 2014: The EU imposes economic sanctions on Russia, targeting the energy, finance, and defense sectors.
- June 2015: The EU extends the economic sanctions on Russia until January 2016.
- December 2015: The EU extends the economic sanctions on Russia until July 2016.
- June 2016: The EU extends the economic sanctions on Russia until January 2017.
- December 2016: The EU extends the economic sanctions on Russia until July 2017.
- June 2017: The EU extends the economic sanctions on Russia until January 2018.
- December 2017: The EU extends the economic sanctions on Russia until July 2018.
- June 2018: The EU extends the economic sanctions on Russia until January 2019.
- December 2018: The EU extends the economic sanctions on Russia until July 2019.
- June 2019: The EU extends the economic sanctions on Russia until January 2020.
- December 2019: The EU extends the economic sanctions on Russia until July 2020.
- June 2020: The EU extends the economic sanctions on Russia until January 2021.
- December 2020: The EU extends the economic sanctions on Russia until July 2021.
- March 2021: The EU imposes sanctions on Russian officials over the imprisonment of opposition leader Alexei Navalny.
- March 2021: The EU imposes sanctions on four Russian officials over human rights abuses in Crimea.
- March 2021: The EU imposes sanctions on eight Russian officials over their role in the conflict in eastern Ukraine.
- April 2021: The EU imposes sanctions on two Russian intelligence officers over their alleged involvement in a 2014 explosion at an arms depot in the Czech Republic.
- June 2021: The EU extends the economic sanctions on Russia until January 2022.
- September 2021: The EU imposes sanctions on Russian individuals and entities involved in the repression of human rights in Belarus.
- October 2021: The EU imposes sanctions on eight Russian officials over the alleged poisoning of opposition leader Alexei Navalny.
The EU has also imposed sanctions on specific Russian entities and individuals in response to various events and actions, such as cyberattacks and interference in foreign elections. The above list is not exhaustive but provides a broad overview of the major sanctions imposed by the EU on Russia.